PLCs: The Backbone of Modern Control Systems
Introduction to Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs)
In today's world, automation has become an integral part of industrial processes, allowing for increased efficiency, reduced downtime, and enhanced safety. One of the key components in achieving these goals is Programmable Logic Controllers, or PLCs. These versatile devices play a critical role in controlling and regulating various industrial processes by executing complex logic sequences based on pre-programmed instructions. In essence, they serve as the "brain" of your factory floor, ensuring that every step of the manufacturing process is precisely managed and executed without human intervention. Let's delve deeper into what PLCs entail.
The Basics of PLCs
A Programmable Logic Controller consists of a central processing unit (CPU) that executes predefined algorithms stored within the device. This CPU interfaces with a variety of input/output modules, which allow for the acquisition of data from sensors or actuators, and the generation of signals to control physical devices or manipulate variables digitally. PLCs can be configured to handle a broad spectrum of tasks ranging from simple timers and counters to complex control systems involving multiple interconnected subsystems.

Advantages of PLCs
One of the most compelling advantages of PLCs is their ability to automate complex systems with ease. By programming the CPU according to specific procedures and conditions, you can create highly efficient and reliable workflows that minimize errors and maximize output quality. Additionally, PLCs are highly reliable, offering fault-tolerant capabilities that ensure smooth operation even during power outages or other disruptions. They also provide flexibility in terms of program modification and upgrades, making it easy to integrate new technologies or adapt to evolving business requirements.
Application Areas
With their versatility, PLCs can be found across a wide range of industries, including but not limited to manufacturing, energy, and transportation. In manufacturing, PLCs are instrumental in managing production lines, monitoring inventory levels, and coordinating assembly operations. In energy sectors like power generation and distribution, PLCs are used to control power grids, monitor equipment status, and optimize power usage. In transportation, they enable real-time monitoring of vehicle performance metrics, ensuring safe and reliable travel for passengers and cargo.
Maintaining and Troubleshooting PLCs
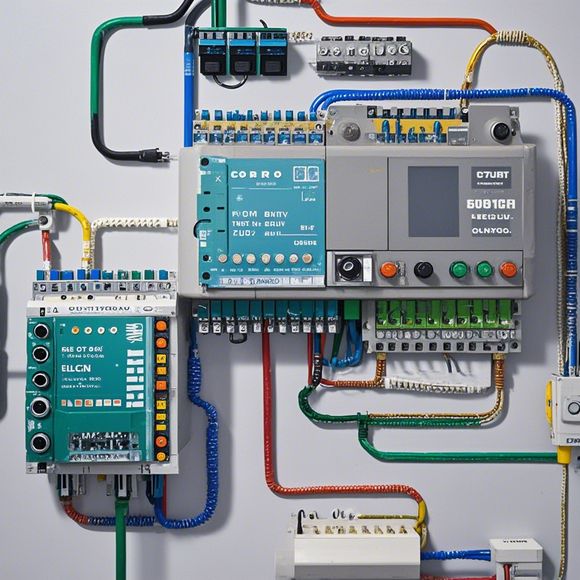
To maintain the functionality and longevity of your PLCs, it's essential to follow best practices for system maintenance and troubleshooting. Regular updates, firmware upgrades, and software patches are crucial to keep the system secure and optimized. Additionally, regular inspections and testing of the hardware components will help identify any potential issues before they escalate into more significant problems. For those encountering technical difficulties, consulting with an expert technician can often resolve issues quickly and effectively.
Conclusion
In summary, Programmable Logic Controllers are the backbone of modern automation systems, enabling seamless control of complex industrial processes with unmatched efficiency, reliability, and flexibility. With their vast array of applications across industries, PLCs remain a cornerstone of modern manufacturing and technological advancement. As such, understanding their basic functions, benefits, and application areas is crucial for anyone looking to streamline their operations or explore new technological opportunities.
Content expansion reading:
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article:
Smart Manufacturing Solutions with PLC Integrated Machinery
The cost of a PLC Controller: A Comprehensive Analysis
PLC Programming for Automation Control in the Manufacturing Industry