plc控制器主机
A Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) is an industrial control system that uses a computer-based microprocessor to manage and control various processes in factories. It allows operators to program the controller for specific functions and automation tasks, which can significantly increase efficiency and reduce downtime. In addition to its use in manufacturing, PLCs are also commonly used in other industries such as healthcare, transportation, and energy. They provide reliable, efficient, and flexible solutions for complex control tasks.
"Mastering the Art of PLC Controllers: A Comprehensive Guide to Mastering the World's Most Important Control Systems"
Introducing the world's most powerful and versatile control systems, PLC (Programmable Logic Controllers). These intelligent machines have revolutionized industries across the globe, from manufacturing and automation to healthcare and energy management. As a seasoned外贸运营, you understand the critical role that efficient PLC controllers play in ensuring smooth operations and maximizing productivity. In this guide, we will delve into the intricacies of mastering these advanced control systems, providing you with insights into their design, functionality, integration, and application.
The Importance of PLC Controllers:
PLC controllers are the heartbeat of modern industrial automation. They are designed to process complex data streams, execute precise calculations, and respond rapidly to changing circumstances. These controllers enable businesses to optimize their operations, reduce downtime, and improve product quality. In essence, they serve as the brains of the factory floor, making it possible for machines to perform complex tasks without human intervention.
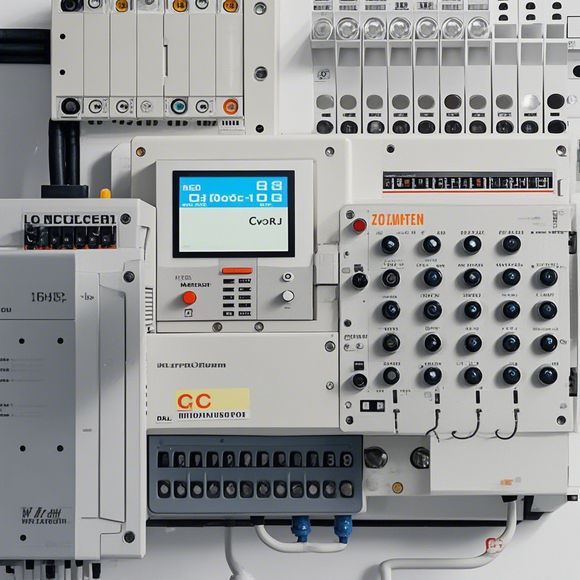

Design and Functionality:
When it comes to designing PLC controllers, manufacturers employ cutting-edge technology to create devices that are both reliable and cost-effective. Each PLC is equipped with multiple input/output ports, enabling it to interface with various sensors and actuators. Moreover, they feature advanced memory capabilities that can store vast amounts of data and instructions, facilitating complex logic programming. Additionally, PLC controllers come in various sizes and configurations, making it easy to tailor them to specific applications.
Integration and Application:
To achieve maximum efficiency, PLC controllers must be integrated seamlessly into the broader industrial network. This involves connecting them to other devices such as sensors, motors, and display screens using appropriate communication protocols like Ethernet or PROFINET. By integrating PLCs effectively, you can create a comprehensive digital ecosystem that enables real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and autonomous decision-making.
Examples of Applications:
1、Manufacturing: PLC controllers are ubiquitous in the manufacturing industry, where they automate processes such as material handling, assembly line control, and quality inspection. For example, in a food processing plant, an PLC can monitor temperature and moisture levels, ensuring that food items reach the right consistency before packaging.
2、Automotive: Vehicle manufacturers use PLCs to control complex systems like engine control units, fuel injection systems, and tire pressure monitoring. One example is the Ford F-Series pickup truck, where an PLC controls everything from the air suspension to the engine performance.
3、Healthcare: In healthcare settings, PLCs are used to manage patient care workflows, monitor vital signs, and control equipment like ventilators. For instance, a PLC can be programmed to adjust the rate of breathing support based on the patient's oxygen saturation levels.
4、Energy Management: In the energy sector, PLCs are essential for monitoring power grid conditions, managing renewable energy sources, and ensuring safe operation. For instance, a PLC can be used to detect faults in wind turbines and switch power to backup generators in case of an emergency.
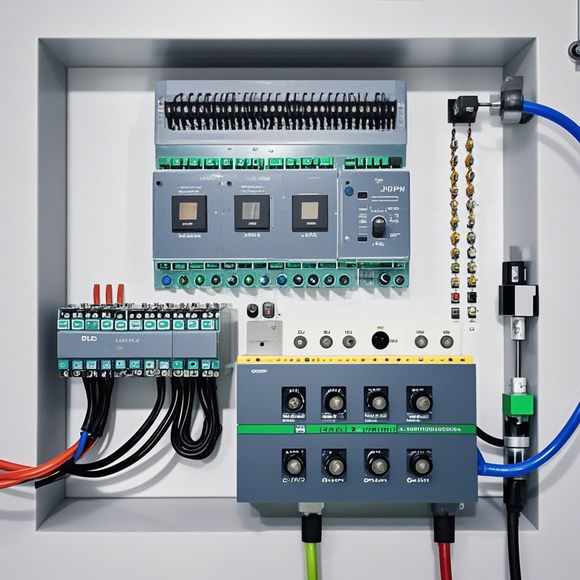

5、Renewable Energy: In areas with abundant solar resources, PLCs are used to optimize energy production by coordinating solar panels, batteries, and storage systems. For example, a PLC can be programmed to shut off solar panels during cloudy days to conserve energy and prevent overheating.
6、Manufacturing Automation: PLCs are used to automate production lines by controlling machines, conveyor belts, and other equipment. For instance, a PLC can be programmed to automatically order materials, set up machines, and adjust production schedules based on demand.
7、Industrial Robotics: In factories equipped with robotic arms, PLCs are crucial for controlling the motion and behavior of the machines. An example could be a machine tool that moves its head to cut parts according to computer-generated instructions.
8、Industrial IoT: In smart factories, PLCs are integrated with Internet of Things (IoT) devices to create a connected ecosystem that collects and analyzes data from a wide range of sensors and devices. For example, a PLC can communicate with a smart thermostat installed in a warehouse, adjusting the temperature to optimize storage conditions based on environmental variables.
9、Industrial Safety: In high-risk environments like oil fields or chemical plants, PLCs are used to monitor safety parameters and ensure compliance with regulations. For instance, a PLC can be programmed to alert personnel if a hazardous gas leak or equipment failure occurs.
10、Agriculture: In agriculture, PLCs are used to manage irrigation systems, fertilizer application, and pest control. For example, a PLC can be programmed to divert water to specific plants based on soil moisture sensor readings.
Customer Support and Services:
As a seasoned外贸运营, understanding customer support and services is crucial when dealing with complex PLC controllers. Here are some tips for ensuring optimal client experience:
1、Proactive Support: Provide proactive customer service by offering regular updates on system performance and any issues encountered. This includes providing troubleshooting guides and answering common questions promptly.
2、Customized Solutions: Tailor your support offerings based on the specific needs of each customer. Offer customization options, such as software upgrades or hardware modifications, to meet individual requirements.
3、Training and Education: Offer training sessions for customers who need to operate and maintain PLC controllers. This helps ensure that clients are confident in using the equipment and can troubleshoot any issues independently.
4、Warranty and Maintenance: Ensure that your warranty policies include coverage for PLC controllers. Offer regular maintenance services to keep your equipment running smoothly.
5、Community Resources: Create a community of users who can share knowledge and experiences with one another. This can help address common issues faced by customers and provide valuable insights into best practices.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, PLC controllers represent a powerful tool for modern industrial automation. By mastering their design, functionality, integration, and application, you can unlock unprecedented levels of productivity and efficiency in your business operations. Don't be afraid to explore innovative solutions and stay ahead of the curve by investing in the latest advancements in PLC controller technology. With our guide at your fingertips, you'll be ready to take your operations to new heights and become a master in the realm of PLC controllers.
Content expansion reading:
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article:
PLC Controller Selection Guide for Foreign Trade Operations
Mastering the Art of Plc Controllers: A Comprehensive Guide to Understand and Implement
PLC Controller for Manufacturing Automation
PLC Programming for Automation Control in the Manufacturing Industry
How to Use a PLC Controller for Your Business
The Role of Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) in Foreign Trade Operations