PLC Controllers for Automated Manufacturing Systems
In an automated manufacturing system, programmable logic controllers (PLC) are crucial for controlling and coordinating various processes. These controllers use a series of instructions to perform tasks such as sequencing machines, monitoring production quality, and adjusting parameters based on the system's output. The PLC is designed to be user-friendly, with clear menus and easy-to-understand screens that make it easy for operators to learn and implement changes quickly. This makes the PLC a popular choice for many industrial applications, including assembly lines and production lines. Overall, PLC controllers play a critical role in ensuring the efficiency and reliability of automated manufacturing systems.
In the modern age of industrial production, automation and precision are the buzzwords that define the future of manufacturing. One of the key components in any automated system is the PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) controller. These devices play a crucial role in managing complex processes, ensuring consistent quality and efficiency. In this guide, we will delve into the intricacies of using PLC controllers in an automated manufacturing system, providing practical insights and tips to help streamline your operations.
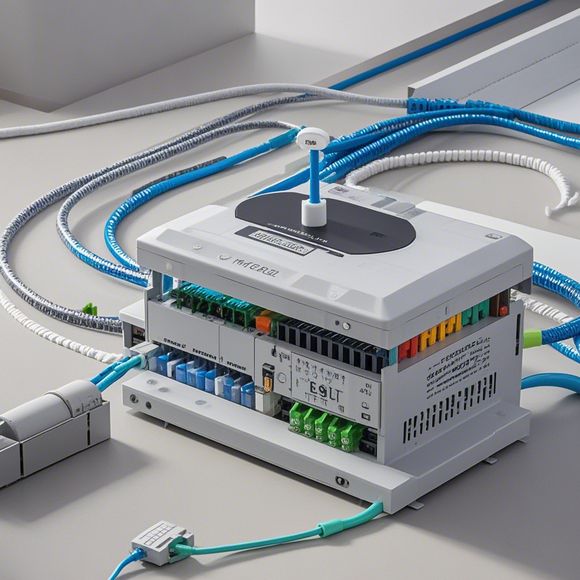

Firstly, let's understand what a PLC controller is and why it is so essential in manufacturing processes. A PLC controller is a programmable device that can execute instructions based on pre-programmed algorithms. It has become a ubiquitous part of many industries due to its ability to handle complex calculations and data processing. In manufacturing, a PLC controller can be programmed to monitor sensor data, control machinery movements, and adjust process variables accordingly. This makes it a valuable asset in maintaining consistency and reducing downtime, which ultimately leads to cost savings and improved product quality.
Now that we have established the importance of PLC controllers in manufacturing, let's dive deeper into the various applications of these controllers. For instance, in the food industry, PLC controllers are used to manage the assembly line, ensuring that products are produced consistently and accurately. In the automotive sector, they are utilized to control engine operations and tire inflation, improving safety and efficiency. Additionally, the pharmaceutical industry relies heavily on PLC controllers for drug production, where precise measurements and controlled temperature conditions are critical for the quality of final products.
When it comes to choosing the right PLC controller, several factors need to be taken into consideration. Firstly, the programming language should be compatible with the hardware platform being used. Secondly, the controller should be able to handle the specific tasks required by the manufacturing process. Thirdly, it is essential to consider the reliability and maintenance requirements of the PLC controller. Fourthly, the cost of the controller should be balanced against the benefits it provides, considering the overall cost of ownership.
Once a PLC controller is chosen, integrating it with other systems within a manufacturing facility requires careful planning and coordination. The most common integration method is through the use of communication protocols such as Ethernet or Modbus. These protocols enable the transfer of data between the PLC controller and other systems within the manufacturing facility. Additionally, software development tools like LabVIEW or MATLAB/Simulink can be used to develop custom solutions that integrate with different types of equipment and processes.
Another aspect to consider when integrating a PLC controller is safety features. In many industrial settings, there are strict regulations regarding worker safety, and PLC controllers must be designed to meet these requirements. Some common safety functions include emergency stop mechanisms, fault detection and isolation, and overload protection. By incorporating these features into the design of the PLC controller, manufacturers can ensure that their processes are safe and reliable for both employees and customers.
Finally, ongoing training and maintenance for PLC controllers is critical for maintaining optimal performance and preventing downtime. Regular updates and patches can address new vulnerabilities and improve functionality. Additionally, regular maintenance checks can help identify potential issues before they become major problems, saving time and money in the long run.
In conclusion, PLC controllers are an integral component of modern manufacturing processes that require careful planning and integration to ensure optimal performance. From choosing the right controller to integrating with other systems, implementing safety measures, and conducting regular maintenance, manufacturers must pay close attention to these aspects to maintain productivity and minimize downtime. With the right approach, PLC controllers can transform even the most complex manufacturing processes into efficient and reliable operations.
Content expansion reading:
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article:
Mastering the Art of Plc Controllers: A Comprehensive Guide to Understand and Implement
PLC Programming for Automation Control in the Manufacturing Industry
The Role of Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) in Foreign Trade Operations
What is a Programmable Logic Controller (PLC)
PLC Controller Advantages: A Comprehensive Guide for Success in Global Trade
Mastering the Art of PLC Control: Unlocking Industry-Grade Automation Powerhouses