PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) Control System Overview
Sure, I can provide an overview of PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) Control Systems. PLC is a type of electronic control system that is used in many industrial applications. It is designed to perform complex tasks such as monitoring and controlling the flow of materials, adjusting equipment settings, and managing automation systems. Unlike traditional mechanical systems, PLCs use software to control hardware instead of relying on physical mechanisms. This makes them highly reliable and flexible, allowing for easy modifications or upgrades as needed.PLC systems are often used in manufacturing processes, where they can be programmed to perform specific functions automatically. For example, a PLC might control a conveyor belt to move materials through a production line, or adjust temperature settings for a bakery oven. In addition to these industrial applications, PLCs are also used in other fields such as healthcare and transportation.Overall, PLC Control Systems are becoming increasingly important in modern industrial environments due to their ability to automate complex tasks with ease and precision.
Introduction:
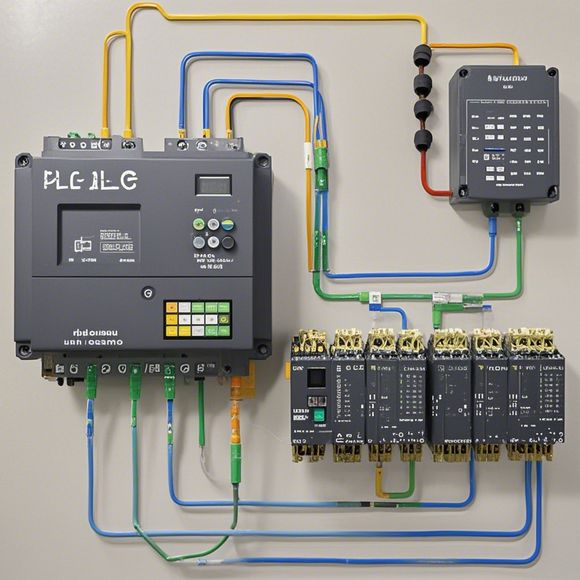
Welcome to our discussion on the PLC control system, which stands for Programmable Logic Controller. This technology is widely used in various industries due to its ability to automate complex processes efficiently and reliably. In this tutorial, we will delve into the working principles of PLCs, their components, functionalities, benefits, and how they integrate with other automation systems. Let's begin!
Components of a PLC:
A typical PLC consists of several key components that work together to perform its functions. These components include:
1、Central Processing Unit (CPU): The brain of the PLC, it executes instructions stored in the program memory and coordinates the activities of the other components.
2、RAM (Random Access Memory): It temporarily stores data needed for processing by the CPU during the execution of a program.
3、Program Memory (EPROM or Flash): This component holds the software programs that the CPU runs. When the power is turned off, the content of the EPROM/Flash is permanently stored.
4、Input/Output Modules: These modules connect external devices such as sensors, actuators, and other equipment to the PLC through digital signals. They convert analog inputs from sensors into binary signals, which can be processed by the CPU, and vice versa for output signals.
5、Power Supply: The power supply module ensures that the PLC operates on an appropriate voltage and current level. It also includes circuitry to manage power-on resets and protection against overvoltage and short circuit conditions.
6、Communication Interfaces: PLCs are often connected to external devices via communication interfaces like RS232, RS485, or Ethernet. These interfaces enable the PLC to communicate with other systems, such as computers, industrial networks, and mobile devices.
Functionality of PLCs:

The primary function of a PLC is to process data and perform calculations based on pre-programmed instructions. Here's a breakdown of some of the key functionalities:
1、Automation: PLCs enable the automation of industrial processes by controlling machines, conveyors, pumps, fans, etc., without manual intervention. This reduces downtime, increases productivity, and minimizes errors.
2、Real-Time Monitoring: Most modern PLCs feature real-time monitoring capabilities that allow operators to view process variables and make quick decisions. This improves efficiency and safety in critical applications.
3、Scheduling and Allocation: PLCs schedule and manage tasks based on predefined rules and priorities. This enables efficient resource allocation and prevents conflicts between tasks.
4、Interfacing with Other Systems: Many PLC manufacturers provide software development kits (SDKs) that allow them to interface with other systems like HMI (Human Machine Interface) displays, SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems, and other industrial automation devices.
Benefits of PLCs:
1、Cost-Efficiency: PLCs offer a cost-effective solution for automation because their hardware costs are relatively low compared to traditional mechanical controllers. Additionally, they require fewer skilled laborers and lower maintenance requirements.
2、Reliability: PLCs have a high degree of reliability due to their built-in redundancy features, which ensure that if one component fails, the rest continue to operate normally.
3、Scalability: PLCs can be easily expanded by adding more processors, RAM, or input/output modules, which allows businesses to meet growing demands for automation without having to invest in new hardware.
4、Compatibility: PLCs are compatible with a wide range of industry standards and protocols, making them easy to integrate into existing systems. This helps businesses streamline operations while reducing integration costs.

Integration with Other Automation Systems:
1、HMI Panels: PLCs can communicate with Human Machine Interface panels to provide intuitive visual feedback to operators. This enhances user experience and makes it easier for nontechnical staff to manage complex systems.
2、SCADA Systems: Many PLCs come with integrated functionality for Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition systems (SCADA). This allows for remote monitoring and control of industrial processes, improving efficiency and security.
3、Internet of Things (IoT): As IoT technologies become more prevalent, many PLCs now support connectivity to the Internet of Things. This enables the integration of real-time data from sensors and devices into centralized management platforms.
4、Cloud-Based Automation: With cloud-based automation solutions, PLCs can be accessed remotely from anywhere using cloud-based clients. This enables businesses to optimize their workflows and reduce overhead expenses.
Conclusion:
In summary, PLCs are powerful tools that have revolutionized the way industries automate their processes. By providing efficient, reliable, and cost-effective solutions, they have become indispensable in industries ranging from manufacturing to healthcare to energy. As technological advancements continue to push the boundaries of automation, the importance of PLCs will only continue to grow. So let's embrace these intelligent devices and take advantage of their capabilities to achieve greater success in our operations!
Content expansion reading:
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article:
PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) Control System Basics
The Role of Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) in Foreign Trade Operations
Connecting a PLC Controller to Your Computer
PLC Controllers: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Their Prices