Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) in Automation and Industrial Process Control
Sure, here's a concise summary of the content you provided in an easy-to-understand English format:"Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) is a crucial component of automation and industrial process control systems. It allows for the implementation of complex logic and control sequences to regulate various industrial processes, such as manufacturing and chemical plants. PLCs can be programmed to perform tasks such as monitoring, controlling, measuring, and recording data, allowing for precise and efficient operations within industrial settings."
In today's manufacturing and industrial sectors, the use of programmable logic controllers (PLCs) is ubiquitous. These advanced digital control systems are instrumental in streamlining processes, increasing efficiency, and ensuring consistent quality across a wide range of applications. From small workshops to large factories, PLCs have become an indispensable tool for managing complex industrial workflows.
At the heart of a PLC system lies its programming capability. Unlike traditional analog controllers that rely on fixed inputs and outputs, PLCs offer a flexible framework that allows programmers to tailor solutions to specific industrial requirements. By writing programs in high-level languages like ladder diagramming or function blocks, engineers can define complex logic sequences with precision. These programs can then be downloaded to the PLC's internal memory and executed as needed, allowing for real-time adjustments based on data input or external conditions.
One of the key benefits of PLCs is their ability to process a vast array of sensor data. Many industrial processes require monitoring and analysis of variables such as temperature, pressure, flow rates, and more. PLCs are designed with advanced sensor interfaces that can seamlessly integrate with these devices, enabling them to collect real-time data that can be used to make informed decisions about production processes. For example, a machine tool may incorporate PLCs that monitor the wear of cutting tools and adjust settings accordingly to maintain optimal performance. Similarly, a chemical plant might have PLCs that monitor levels of reactants and automatically adjust the mixing ratio if concentrations deviate from safe limits.
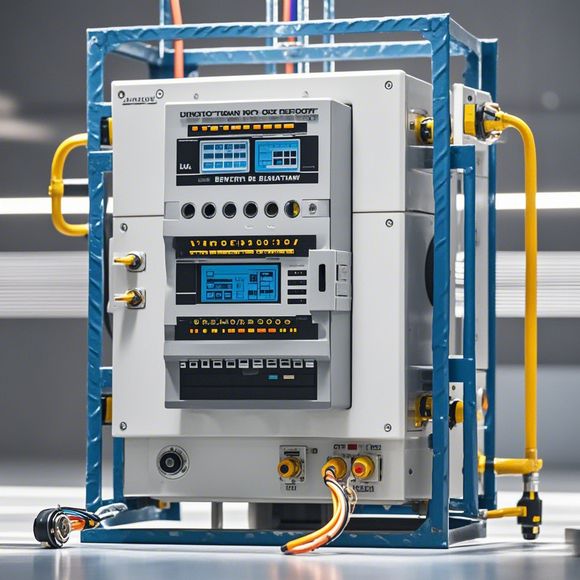

Another crucial aspect of PLC functionality is their robustness in handling faulty situations. In environments where machinery and equipment are prone to breakdowns, having a reliable system capable of quickly identifying and mitigating problems becomes critical. PLCs are equipped with built-in redundancy mechanisms, such as dual processor configurations or networked systems that can share data and operate independently in case of hardware failure. This ensures that even when one PLC fails, the remaining units can continue to function safely. Moreover, many PLCs include safety features like overcurrent protection, grounding, and alarm systems, which further enhance safety margins in hazardous environments.
The integration of PLCs with other automation technologies is also noteworthy. With the advent of Industry 4.0, modern PLCs are increasingly integrated with other smart manufacturing systems such as computer numerical controlled (CNC) machines, robotics, and cloud computing infrastructure. This interconnectivity enables seamless communication between different components, enabling true automation of entire workflows. For instance, an assembly line might use a PLC to manage the sequence of operations involving multiple CNC machines, ensuring that parts are precisely aligned and assembled in the correct order without human intervention.
Moreover, advancements in IoT technology have further enhanced the capabilities of PLCs. The Internet of Things (IoT) allows for real-time connectivity between PLCs and various types of devices, enabling remote monitoring and control. This not only improves operational efficiency but also enables predictive maintenance by analyzing data patterns and predicting potential issues before they arise. For example, a factory might have PLCs monitoring temperature and humidity within its HVAC system, using IoT sensors to detect any irregularities that could indicate a problem with heating or ventilation systems.
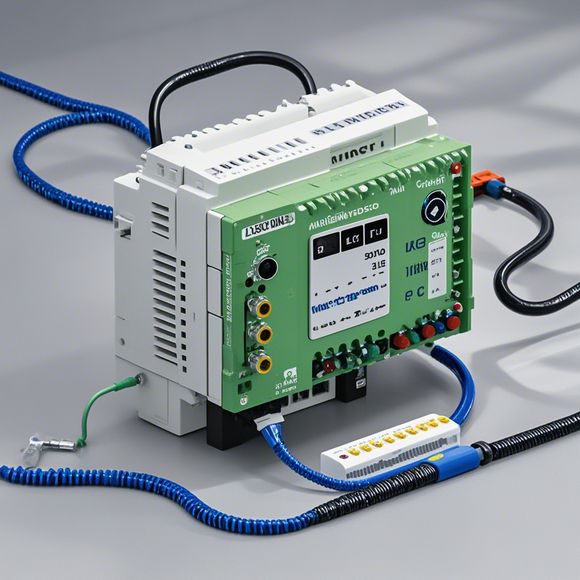

Despite their impressive functionalities, there are several considerations to keep in mind when selecting and implementing PLC solutions. One critical factor is the need for skilled personnel who can effectively program and troubleshoot these sophisticated systems. Additionally, the cost of acquiring and maintaining a PLC system can be significant, particularly in larger facilities. Therefore, it is essential to conduct thorough cost-benefit analyses to determine whether the benefits of PLC implementation outweigh the associated costs.
Another important consideration is the regulatory environment. Many industries have stringent standards for safety and compliance with regulations like ISO 9001 or OSHA standards. As such, it is critical to ensure that PLC systems comply with relevant regulations before integrating them into any production process. This may involve obtaining certification or consulting with experts familiar with the local regulatory landscape.
In conclusion, PLCs represent a vital component of modern industrial automation. Their ability to process complex sensor data, handle faulty situations reliably, and integrate with other advanced technologies makes them an essential tool for achieving efficient and safe industrial production. However, their adoption requires careful planning, expertise, and adherence to industry best practices. By understanding the full spectrum of their capabilities and considering the necessary considerations, businesses can harness the power of PLCs to achieve unparalleled levels of productivity and innovation.
Content expansion reading:
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article:
How to Use a PLC Controller for Your Business
Plumbers Rule! The Role of PLC Controllers in the World of Waterworks
The Role of Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) in Foreign Trade Operations
Connecting a PLC Controller to Your Computer
PLC Controllers: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Their Prices