PLC Controller Full Set
The PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) is a device that can control and manage industrial processes by executing programs stored in its memory. It's often used in manufacturing, automation, and other industrial environments to automate tasks such as lighting, temperature regulation, and machine operations. The "Full Set" of the PLC means that it has all the features needed to perform its job effectively, including input/output devices for monitoring, controlling, and communicating with various systems. This makes it a powerful tool for any industry where precision and efficiency are crucial. Whether you're working on a small scale or large-scale projects, an PLC Full Set can help streamline your operations and improve overall productivity.
As a professional in the field of foreign trade operations, I am responsible for managing and ensuring the smooth flow of goods and services between different parties. In this role, it is essential to have a comprehensive understanding of the various components that make up a PLC controller system, which stands for Programmable Logic Controller. Here are some key aspects of PLC controllers that I would like to discuss in detail:
1、What is a PLC Controller?
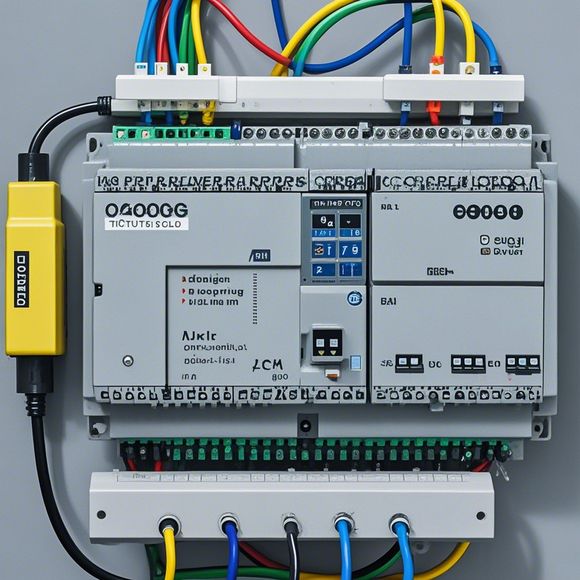
PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers) are computerized devices designed to control and monitor industrial processes. Unlike traditional analog or digital systems, they can be easily programmed with complex algorithms to perform specific functions such as temperature control, process monitoring, and machine control.
2、Components Inside the PLC Controller System:
Processor Unit (CPU): The brain of the PLC, it interprets commands from the user interface and executes them through a set of instructions stored in the memory.
Input/Output Modules: These modules provide connectivity to external devices like sensors, switches, and valves, allowing the PLC to read data from these devices and send commands to them.
Memory: This component stores the program code that the CPU executes, enabling it to run multiple programs simultaneously without needing reprogramming each time.
Power Supply Unit: It provides electricity to the entire PLC system, including the processor unit, input/output modules, and other peripherals.
Clock: An electronic device that generates a precise sequence of pulses that the PLC uses to determine the current time and ensure synchronization between modules.
3、How PLCs Work:
To operate effectively, a PLC must first receive commands from the operator's control panel or a remote device. Once these commands are received, the PLC's CPU interprets them according to its program and then executes the necessary actions, such as opening a valve or setting a temperature control.
4、Advantages of PLCs:
Robustness: PLCs can withstand harsh environments and operate efficiently even in conditions with high noise levels.
Flexibility: They can be customized to meet the specific needs of any industry, from manufacturing to healthcare.
Safety: By controlling critical functions like pressure and temperature, PLCs can significantly reduce the risk of accidents caused by human error.
5、Choosing the Right PLC:
Functionality: Determine what features are needed based on the process you want to automate.
Communication: Consider factors such as the number of inputs/outputs and the types of communication protocols used.
Programming Language: Different manufacturers may offer programming languages like Ladder Diagram, Function Block Diagram, or Structured Text. Choose the one best suited to your team’s skills.
Price: While cost should not be overlooked, it’s important to find an affordable solution that meets all the requirements.
6、Maintenance and Support:

Regular Checks: Keep the system clean and free of dust and debris to ensure optimal performance.
Updates: Stay informed about new software versions and updates to improve system security and performance.
Training: Ensure that all users are well-versed in using the PLC controller system.
7、Case Study:
Let’s say we have a chemical processing plant that needs to monitor and control several variables such as temperature, pressure, and flow rate. With the help of a PLC controller, we can create a comprehensive monitoring system capable of alerting us when any parameter deviates from safe operating ranges. This not only ensures product quality but also reduces downtime due to unexpected events.
8、Conclusion:
PLC controllers are an essential part of modern industrial automation, providing efficient, reliable, and safe solutions for industries across various sectors. As our focus continues to evolve, embracing the latest advancements in technology will undoubtedly enhance our ability to optimize production processes and drive efficiency.
In summary, let’s take stock of our discussion regarding the PLC controller system:
The PLC Controller System: A comprehensive guide that covers everything you need to know about PLC controllers, including their key components and how they work to streamline industrial processes across various industries.
Components Inside the PLC Controller System: Discuss the various components inside the PLC controller system, such as the processor unit (CPU), input/output modules, memory, power supply unit, and clock.
How PLCs Work: Analyze how PLCs operate by receiving commands from the operator's control panel or a remote device, interpreting them according to the program, and executing the necessary actions.
Advantages of PLCs: Discuss the advantages of using PLCs in various industries, including their robustness, flexibility, and safety.
Choosing the Right PLC: Offer guidance on choosing the right PLC based on functional requirements, communication protocols, programming language, and cost considerations.
Maintenance and Support: Share tips on regular checks, updates, and training to ensure the longevity and effectiveness of PLC controller systems.
Case Study: Use a real-world example to illustrate the importance of PLC controllers in chemical processing plants.
Conclusion: Reiterate the importance of adopting cutting-edge technologies in optimizing production processes and driving efficiency.
Overall, by understanding and utilizing these key points, we can confidently navigate the complex world of industrial automation and achieve greater success in our endeavors.
Content expansion reading:
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article:
PLC Controller Selection Guide for Foreign Trade Operations
PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) Control System Basics
The Role of Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) in Foreign Trade Operations
Connecting a PLC Controller to Your Computer
PLC Controllers: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Their Prices