PLC Controllers: A Revolution in Managing Industrial Processes Automation
PLC控制器是工业自动化领域的一次巨大变革。它们能够实时处理复杂的工业过程,使得生产过程更加精准、高效。PLC控制器通过其内部的微型电脑系统,对生产过程中的各种参数进行实时监控和调整,确保生产过程的稳定运行。这使得工业生产的灵活性大大提高,同时也降低了生产成本和能源消耗。
Introduction:
In the realm of industrial automation, process control logic has always been at the heart of manufacturing efficiency. One of the most crucial components of these control systems is the programmable logic controller (PLC). PLCs are devices that can be programmed to perform various functions based on a pre-existing algorithm or sequence of commands. They have become an integral part of modern industrial environments due to their ability to handle complex tasks with precision and reliability. This essay will delve into the working principles of PLCs, their applications, benefits, and limitations to provide a comprehensive understanding of this powerful technology in industrial automation.
Working Principles:
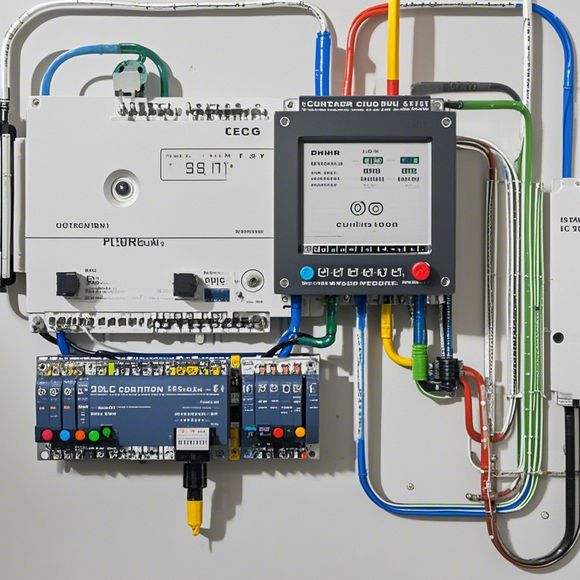
The working principle of PLCs is based on microprocessors that process input signals and generate output signals to control physical devices. These microprocessors are housed in a small box known as a PLC board, which is connected via cables to various sensor inputs, actuator outputs, and other external devices. The microprocessor executes software instructions stored in the PLC's memory, which then generates the appropriate signals for the physical devices.
PLCs are designed to be highly resilient and can withstand harsh operating conditions, such as high temperatures, dust, and vibration. They are also equipped with features such as overload protection, fault detection, and diagnostic monitoring, which ensure their safety and longevity in industrial environments. Additionally, PLCs come with various programming languages, such as Ladder Diagram (LD), Function Block Diagram (FBD), or Structured Text (ST), making them easy to use for different types of industries.
Applications:
One of the primary applications of PLCs is in process control. They are used to regulate and monitor various industrial processes, such as heating and cooling systems, chemical reactions, and pneumatic conveyor systems. PLCs can also be used in manufacturing lines, assembly lines, and other production environments to improve efficiency and quality control.
Another application of PLCs is in industrial automation. They are extensively used in robotics, where they are responsible for controlling the movements of industrial robots. PLCs can also be integrated with other automation technologies such as SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems and HMI (Human Machine Interface) devices for more advanced automation solutions.
Benefits:
The benefits of using PLCs include increased efficiency, reduced downtime, improved safety, and enhanced flexibility. PLCs can be programmed to perform specific functions, reducing the need for manual intervention and increasing productivity. They are also less prone to human error, making them ideal for critical applications where accuracy is essential.
In addition to these advantages, PLCs offer significant cost savings through their ability to automate complex processes. By automating individual operations, they can reduce labor costs and eliminate wasteful manual tasks. Furthermore, PLCs can be easily customized and upgraded to meet changing industry needs, ensuring long-term cost savings.
Limitations:
Despite their numerous benefits, PLCs do have some limitations. One of the main disadvantages is the lack of direct communication capabilities with other systems. This means that PLCs must be interfaced with other devices using dedicated hardware or software protocols. Additionally, PLCs may not be compatible with all types of hardware and software, leading to potential compatibility issues when integrating them with new equipment.

Another limitation is the lack of real-time monitoring capabilities. While modern PLCs can provide accurate data, they may not be able to display information in real-time, which can be a hindrance when monitoring critical processes. Finally, the learning curve associated with programming PLCs may be steep for some users, requiring specialized expertise to fully leverage their capabilities.
Future Developments:
Looking towards the future, there is great potential for advancements in the development of PLCs. One area of focus is the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) technologies with PLCs. AI can help PLCs learn from past experiences and optimize their performance over time, improving overall efficiency and accuracy. ML can also enable PLCs to make more accurate predictions and decisions based on complex data sets.
Another exciting development is the integration of IoT (Internet of Things) technologies with PLCs. By connecting IoT devices to a network, PLCs can gather real-time data on industrial processes and make informed decisions based on this data. This can lead to improved efficiency, reduced downtime, and enhanced safety in industrial settings.
Conclusion:
The programmable logic controller (PLC) has revolutionized the way industrial processes are automated. Its ability to handle complex tasks with precision and reliability makes it a valuable tool for businesses across various industries. From process control to automation, PLCs offer numerous benefits, including increased efficiency, reduced downtime, improved safety, and enhanced flexibility.
However, like any technological advancement, there are some limitations to consider when implementing PLCs. These limitations may require additional training or specialized equipment for optimal operation. Nonetheless, with continued innovation and advancement in the field of automation, it is clear that PLCs will continue to play a vital role in shaping the future of industrial automation.
Content expansion reading:
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article:
PLC Controller Selection Guide for Foreign Trade Operations
PLC Controller Wiring Guideline
PLC Controller for Manufacturing Automation
The cost of a PLC Controller: A Comprehensive Analysis
How to Use a PLC Controller for Your Business
The Role of Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) in Foreign Trade Operations