plc控制器模块
PLC控制器模块是现代工业自动化中不可或缺的一部分,它通过程序控制方式实现对生产过程的控制。这种设备通常用于自动化生产线、工厂、机器人和工业设备的控制等场景,具有高可靠性、扩展性强和成本低廉等特点。PLC控制器的组成部分包括中央处理器(CPU)、输入模块、输出模块和电源模块等,其中CPU作为PLC的控制中心,通过总线连接存储器和各种接口,以控制它们有序地工作。PLC控制器的主要作用是接收外部的感应信号,通过中央处理器进行逻辑计算和处理,然后输出到执行器(如电机、气缸、阀门)来控制设备的运行状态。其优点包括可编程性、高可靠性、易于扩展和维护等,这使得它在工业生产中得到了广泛应用。在制造业中,PLC可以用于监控和控制生产线上的各种机械设备;在交通运输领域,PLC可以用于控制火车或飞机的运行状态;在建筑物自动化中,PLC也可以用于管理建筑的电力系统和其他设备。PLC控制器是一种先进的自动化控制装置,它通过程序控制方式实现了对生产过程的高效管理和控制。随着技术的不断发展,PLC控制器的性能和功能也在不断提升,为工业自动化的发展提供了强大的技术支持。
"Exploring the World of PLC Controllers – A Comprehensive Guide for Your Business"
Content:
Hello there! As you embark on your journey into the world of PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) controllers, I'm here to guide you through a comprehensive understanding of this fascinating topic. Whether you're a seasoned industry professional or just starting out, this guide will provide you with all the information you need to make informed decisions and maximize the benefits of these powerful tools.
So, let's dive right into the heart of this topic. First and foremost, what are PLC controllers, and why should you care about them?
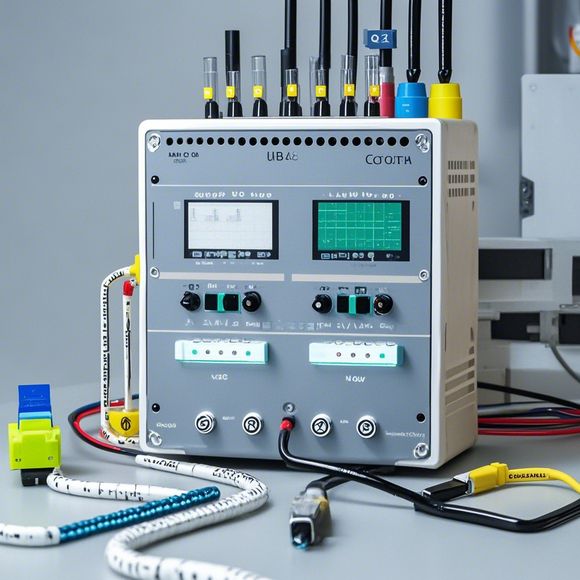

PLCs are digital computers that control industrial processes by executing instructions stored in their memory based on predefined logic. They're designed to handle complex calculations and data processing tasks that would otherwise require human intervention. By using PLCs, businesses can improve efficiency, reduce downtime, and minimize errors, ultimately leading to cost savings and improved product quality.
Now, let's talk about the different types of PLC controllers available in the market today. There are two main categories: analog and digital. Analog PLCs process real-world signals such as temperature, pressure, and flow rates using sensors and other analog components. They're commonly used in applications like heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems. Digital PLCs, on the other hand, process digital signals such as binary numbers and logic gates, making them ideal for more complex control tasks like manufacturing automation and robotics.
As you might expect, each type has its unique advantages and disadvantages. For example, analog PLCs are easier to set up and maintain than digital PLCs, but they may not be able to handle complex algorithms as well. On the other hand, digital PLCs can handle advanced logic and control functions more effectively, but they may require more expensive hardware and software. It's important to consider your specific needs and budget when deciding which type of PLC controller is right for your business.
Once you've decided on the type of PLC you need, the next step is to choose an appropriate controller. There are several factors to consider when selecting a controller, including size, power requirements, connectivity options, and programming languages. For example, if you're working with a large factory, you may want to opt for a controller with a larger memory capacity and more processing power to handle multiple inputs simultaneously. Similarly, if you need to connect to a wide range of devices, you may want to consider a controller with multiple input/output ports and support for various communication protocols like Profibus and Ethernet.
When it comes to programming, PLCs are incredibly versatile and easy to use. Most modern PLCs come with built-in programming software that allows you to create custom programs quickly and easily. This software can be used to define the control logic for your processes, simulate operations before deployment, and troubleshoot any issues that arise. To get started, you'll need to learn about the basic concepts of programming, such as variables, conditions, loops, and functions. Once you have a good grasp of these concepts, you can start building your custom programs and integrating them into your existing workflow.
Another important aspect of PLC programming is safety features. Many modern PLCs come with features designed to ensure the safety of your employees and the environment. These features include emergency stop buttons, fault protection circuits, and user-friendly interfaces that make it easy for operators to identify and respond to potential hazards. By incorporating these safety features into your PLC system, you can significantly reduce the risk of accidents and injuries on-site.
In conclusion, PLC controllers offer a powerful tool for controlling industrial processes with ease and efficiency. By taking the time to research different types and choose the right controller for your needs, you can optimize your operations, save money, and increase productivity. Remember, investing in the right PLC controller can pay off in terms of reduced maintenance costs, improved performance, and increased competitiveness in the marketplace. So, go ahead, dive deeper into this exciting world of PLCs, and discover the endless possibilities for growth and success in your own business.
Content expansion reading:
Content:
Welcome to the exciting world of PLC controllers! Whether you're a budding automation enthusiast or a professional looking to expand your knowledge, this guide is designed to help you navigate the ins and outs of programmable logic controllers. Let's dive in and uncover everything you need to know to get started!
What is a PLC Controller?
PLC stands for Programmable Logic Controller. Essentially, it's a type of industrial computer designed to automate various electromechanical processes. Unlike traditional computers, PLCs are built to withstand harsh industrial environments, with features like real-time operation, high reliability, and ease of programming.
Why Use PLC Controllers?
PLCs offer several advantages over hard-wired relay logic or manual operation:
1、Automation: PLCs can automate repetitive tasks, reducing the need for human intervention and increasing efficiency.
2、Flexibility: With PLCs, you can easily modify or expand your control system as your needs change, simply by reprogramming the controller.
3、Safety: PLCs can monitor and control equipment to ensure safe operation, often incorporating safety features such as interlocking and emergency stop functions.
4、Reliability: PLCs are built to operate continuously for long periods, with minimal maintenance required.
Types of PLC Controllers
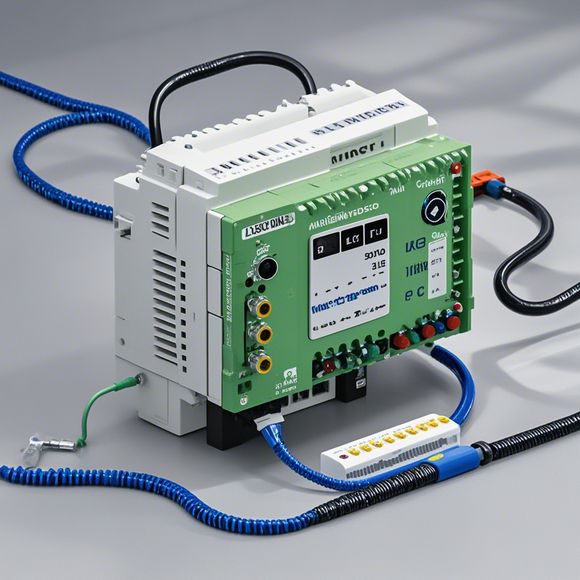

PLCs come in various types, each designed for specific applications:
Fixed I/O PLCs: These are the most common type, with a fixed number of input and output points.
Modular PLCs: These allow you to add I/O modules as needed, making them scalable and suitable for larger systems.
Compact PLCs: These are smaller, less expensive versions of PLCs, often used for simple control tasks.
Micro PLCs: These are the smallest and most cost-effective PLCs, designed for very basic control applications.
PLC Components
A PLC typically consists of several key components:
CPU (Central Processing Unit): The brain of the PLC, responsible for executing the program and making decisions based on the input data.
Memory: Stores the program, user data, and system files.
Input/Output (I/O) Modules: These modules interface with the process by receiving signals from sensors and actuators.
Power Supply: Provides the necessary power to the PLC and its connected modules.
Communication Ports: Allow the PLC to communicate with other devices, such as computers, HMIs, and other PLCs.
Programming PLC Controllers
PLCs are programmed using a variety of languages and software:
Ladder Logic: The most common programming language, which resembles electrical ladder diagrams.
Function Block Diagram (FBD): A graphical language that uses function blocks to represent operations.
Sequential Function Chart (SFC): Used for complex operations that require a sequence of steps.
Structured Text (ST): A text-based programming language similar to Pascal or Basic.
Programming software is provided by PLC manufacturers and often includes tools for debugging and simulation.
Installing and Configuring a PLC
Installing a PLC involves:
1、Mounting: Installing the PLC in a suitable enclosure or panel.
2、Wiring: Connecting the PLC to the power supply and I/O devices.
3、Configuration: Setting up the PLC with the appropriate I/O modules and configuring the communication settings.
4、Programming: Writing the control logic using the programming software.
5、Testing: Verifying that the PLC is functioning correctly by running tests and simulations.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance includes checking the PLC for signs of wear, ensuring proper cooling, and updating the firmware if necessary. Troubleshooting involves using diagnostic tools to identify and resolve issues with the PLC or the connected devices.
Applications of PLC Controllers
PLCs are used in a wide range of industries, including:
Manufacturing: For controlling production lines and assembly processes.
Automotive: For managing the complex sequences of an automobile assembly.
Water Treatment: For monitoring and controlling water treatment plants.
Energy: For managing power generation and distribution systems.
Building Automation: For controlling HVAC systems, lighting, and security.
Choosing the Right PLC
When selecting a PLC, consider factors such as the number of I/O points, the type of inputs and
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article:
The cost of a PLC Controller: A Comprehensive Analysis
PLC Programming for Automation Control in the Manufacturing Industry
How to Use a PLC Controller for Your Business
PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) Control System Basics
Plumbers Rule! The Role of PLC Controllers in the World of Waterworks