plc接线及原理图
根据您提供的内容,以下是一段口语化英文摘要:The Plastics Control Panel (PLC) is an essential device in industrial automation. Its primary functions include processing and controlling various processes, such as motor control, process control, and safety protection systems. The PLC connects to various devices through specific interfaces, including sensors, actuators, and other input/output components. In terms of connection, it uses a variety of methods depending on the type of device and the application requirements. For instance, buttons and switches can be connected directly, while temperature sensors may require more complex wiring or integration with signal processing units.The PLC also has a memory system that stores system-specific software, user programs, and data needed for operations. This ensures that the PLC can perform tasks without reliance on external hardware or direct human intervention. The communication capabilities of the PLC are diverse, including both analog and digital signals. Some common connections include RS-485 protocol for remote monitoring and control systems, which can extend the range of the system and improve efficiency.In summary, the PLC plays a crucial role in modern industrial automation, providing reliable and efficient solutions for process control and automation needs. Its ability to integrate different types of devices and communicate effectively allows for flexibility in application settings and adaptability to various production environments.
"Introduction to PID Control System: Understanding PLC Connection and Operational Principles for Optimal Process Management"
Industry-specific Content:
When it comes to running an industrial plant or any other manufacturing facility, there are a few key components that need to function seamlessly. One of these is the Programmable Logic Controller (PLC), which is responsible for monitoring and controlling various processes in your facility. In this guide, we'll delve into the world of PLC wiring and its operational principles to help you understand how it works and how to effectively utilize it to manage your manufacturing processes.

First things first, when you're dealing with PLCs, it's crucial to have a solid understanding of what they are capable of doing. A PLC is essentially a computer that can be programmed to perform specific tasks based on inputs from sensors, actuators, and other hardware devices. It's designed to work with a variety of different types of sensors and motors, allowing you to control almost any aspect of your production process.
Now let's talk about the connections involved in PLC wiring, which are just as important as the actual operation of the device itself. The primary connection between the PLC and other devices is through the input/output (I/O) modules. These modules allow you to connect sensors and actuators to the PLC, providing real-time data to the controller. This is where you will find the majority of your wiring, with each module typically having a dedicated power source and a set of wires that connect to other modules within the system.
As you begin working with PLCs, one important thing to keep in mind is that each module has a unique address, which is used by the PLC to identify and interact with the device at a specific location on the network. This means that when you're connecting different modules to the same PLC, you must ensure that their addresses are properly assigned so that the PLC can communicate with them correctly.
Another important aspect of PLC wiring is the use of relays, which are often used in conjunction with PLCs to control motors and other equipment. Relays are electrical switches that can be activated remotely, allowing you to turn off or activate motors and other devices without physically disconnecting them from the main power supply. When wiring relays to a PLC, it's essential to consider their maximum current and voltage ratings, as well as the type of contacts required to safely connect to the PLC.
One of the most critical aspects of PLC wiring is ensuring that all connections are properly grounded. Grounding is essential not only for safety reasons but also for preventing electrostatic discharges that could damage sensitive electronic components. In some cases, you may need to use special grounding cables to ensure that all connections meet the necessary standards for electrical safety.
Once you've completed your PLC wiring, it's time to dive into the operational principles of the device itself. The PID controller is one of the most commonly used types of PLC, which stands for Proportional, Integral, and Derivative. This controller is designed to maintain a stable level of output over time, making it ideal for applications such as temperature control in factories or chemical processes.
The PID controller consists of three main parts: a Proportional (P), Integral (I), and Derivative (D) part, which work together to provide feedback on changes in the process being controlled. The P part measures the difference between the desired output and the actual output, and adjusts the output accordingly. The I part takes into account the amount of time that has passed since the last change and adjusts the output accordingly. The D part calculates the rate of change of the desired output and adjusts it based on this information.
To effectively use the PID controller in your PLC, you must first determine the desired behavior of your process. This involves setting appropriate limits for both the positive and negative outputs, as well as defining how quickly the controller should respond to changes in the process. Once you've established your goals, you can program the PLC to execute a series of commands that will adjust the output according to the rules defined above.
One of the key challenges in using PLCs is ensuring that they remain reliable and accurate over time. To achieve this, it's important to regularly test your PLCs for errors and issues that may arise during normal operation. Additionally, keeping track of maintenance schedules and troubleshooting steps can help prevent problems from becoming more severe down the line.
Ultimately, the success of any industrial plant depends on the careful planning and execution of various components, including PLCs. By understanding the basics of PLC wiring and the operational principles behind the device, you can take full advantage of its capabilities and create a highly efficient and reliable manufacturing environment. So don't be afraid to get hands-on with your PLCs; they are incredibly powerful tools that can make all the difference in your industrial production.
Content expansion reading:
Content:
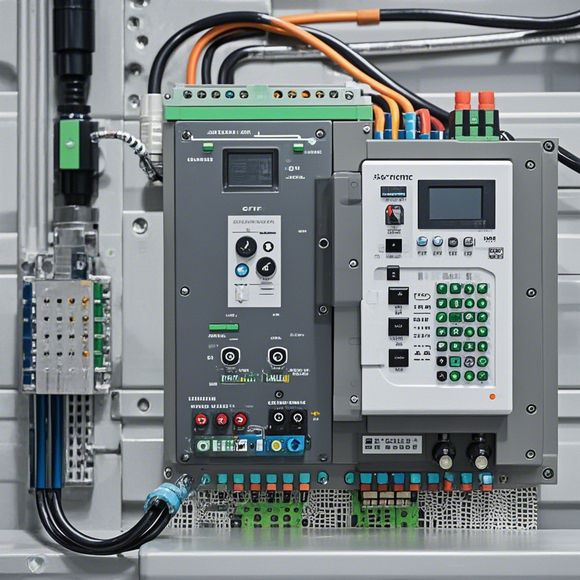
Hey there! So, you're looking to learn more about Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) and how to make sense of those complex wiring diagrams and schematics, right? Well, you've come to the right place! Let's dive in and break it down in a way that's easy to understand.
First things first, what is a PLC? It's a type of industrial computer designed to control and automate various electromechanical processes. They're tough, they're reliable, and they can handle the harsh conditions of a manufacturing environment.
Now, let's talk about wiring. PLCs have inputs and outputs that need to be connected to different devices and sensors. Inputs might be from switches, sensors, or other devices that tell the PLC what's happening in the process. Outputs could be connected to actuators, motors, or lights that the PLC controls.
When you're looking at a PLC wiring diagram, you're essentially looking at a map that shows how all these components are connected to the PLC. It's crucial to follow this diagram carefully when you're setting up your system because even a small mistake can lead to big problems.
Here's a quick rundown of what you might see on a typical PLC wiring diagram:
1、Power Supply: This is where the PLC gets its juice. Make sure you're using the correct voltage and that the power supply is properly grounded.
2、Inputs: These are your switches, sensors, and other devices that send signals to the PLC. They're usually labeled with a "I" for input.
3、Outputs: These are the devices that the PLC controls, like relays, solenoids, or lights. They're labeled with an "O" for output.
4、CPU: This is the brain of the PLC. It's where all the magic happens, processing the inputs and controlling the outputs.
5、Memory: This is where the PLC stores its programs and data. Different types of memory are used for different purposes.
6、Communication Ports: These are how the PLC talks to other devices, like computers or other PLCs.
7、Battery: Some PLCs have a battery backup to keep the memory alive in case of a power failure.

8、Terminal Blocks: These are the connectors where you actually wire everything up. They can be DIN rail mounted or panel mounted.
Remember, when you're wiring up your PLC, safety is key. Always follow the manufacturer's instructions and local regulations. And if you're unsure about anything, it's always best to consult with a professional.
Now, let's talk about schematics. These are the diagrams that show the electrical circuits within the PLC. They can be a bit more complex than wiring diagrams because they show the internal workings of the PLC itself.
Schematics might include:
Power Circuits: How the power is distributed within the PLC.
Signal Circuits: How the input and output signals are processed.
Logic Gates: These are the electronic circuits that perform logical operations.
Timers and Counters: These are used to control the timing and sequence of operations.
To understand a PLC schematic, you need to have a basic knowledge of electrical engineering and electronics. It's not something you're expected to master overnight, but with a bit of practice and some background reading, you can start to make sense of them.
And that's the gist of it! Understanding PLC wiring and schematics is a valuable skill in the world of automation. It's all about taking the time to learn the language of the diagrams and then applying that knowledge to ensure your systems are running smoothly and safely.
So, grab a cup of coffee, maybe a highlighter, and start studying those diagrams. Before you know it, you'll be reading them like a pro!
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article:
PLC Controller for Manufacturing Automation
The cost of a PLC Controller: A Comprehensive Analysis
PLC Programming for Automation Control in the Manufacturing Industry
The Role of Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) in Foreign Trade Operations
Connecting a PLC Controller to Your Computer
PLC Controllers: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Their Prices