PID Controller Overview
PID controller stands for Proportional-Integral-Derivative controller. It is a type of feedback control system used to regulate the output signal of a process. This controller calculates the error between the desired output and the actual output, and adjusts the control signal accordingly. The three parts of PID control are: 1. Proportional (P): This part of the PID controller calculates the error in a linear manner, giving the control signal directly proportional to the error. If there is an error in the output, the control signal will increase to reduce the error.,2. Integral (I): This part of the PID controller calculates the sum of all errors over time. The integral term gives the control signal a memory component that reduces over time as the error decreases. This helps to smooth out sudden changes in the output.,3. Derivative (D): This part of the PID controller calculates the rate of change of the error. The derivative term gives feedback to the control signal to quickly respond to changes in the error. This helps to eliminate steady-state errors and provides a faster response than the other parts of the PID controller.
Introduction:
In today's ever-evolving world, the role of a plc controller has become increasingly significant in various industries. From manufacturing to healthcare, from transportation to energy generation, plc controllers are at the core of many systems that ensure smooth operation and efficiency. This guide aims to provide an overview of what a plc (programmable logic controller) controller is, its components, functions, and applications. By the end of this guide, you will have a comprehensive understanding of how these controllers work and how they can benefit your business. So, let's dive right in!
Components:
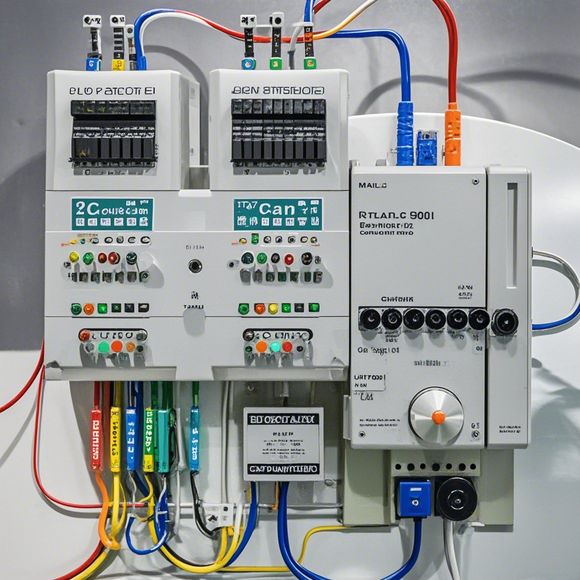
A plc controller is a powerful computer system designed to process data and instructions generated by other devices within a manufacturing or industrial environment. It works with other systems such as sensors, actuators, and software to create a complex control system that manages the flow of information throughout a production line or other industrial processes. The main components of a plc controller include:
1、Central Processing Unit (CPU): The CPU is the brain of the controller and performs various functions such as processing data, executing instructions, and managing memory.
2、Input/Output Devices: These devices enable communication between the controller and external devices such as switches, sensors, and displays.
3、RAM and ROM: These are temporary and permanent storage devices that store data used by the CPU for calculations and execution of instructions.
4、Power Supply: This device provides the necessary power to operate the CPU and other internal components of the controller.
5、Network Connection: This enables communication between the controller and other devices in the same network, such as computers or other plc controllers.
Functionality:
The functionality of a plc controller is based on a series of algorithms that it executes to control the behavior of the system. Some of the key functions include:
1、Data Acquisition: The controller collects data from sensors and other input devices, which may be used to monitor and measure physical quantities such as temperature, pressure, or speed.
2、Process Control: The controller determines the optimal settings for various variables such as temperature, flow rate, and pressure based on measured data and predefined goals. This allows for precise control of production processes.
3、Safety Features: Many plc controllers incorporate safety features such as emergency stop buttons, overload protection, and fault detection circuits to prevent accidents and protect personnel.

4、Scheduling and Alarming: Some controllers also include advanced features such as timers, alarms, and event logging to schedule tasks and monitor equipment status.
Applications:
The plc controller has numerous applications across various industries, ranging from manufacturing to energy generation. Some of the common applications include:
1、Industrial Automation: In manufacturing, plc controllers are used to automate production lines, optimize production processes, and improve overall efficiency. They can control machines, robots, and other equipment to achieve high-quality output while reducing costs and downtime.
2、Healthcare: In healthcare, plc controllers are used to control medical equipment such as ventilators, infusion pumps, and surgical instruments. They can also help manage patient monitoring systems and assist in the diagnosis and treatment of patients.
3、Agriculture: In agriculture, plc controllers are used to control irrigation systems, fertilizer dispensers, and other equipment. They can optimize water usage, improve crop yield, and reduce waste.
4、Energy Generation: In energy generation, plc controllers are used to manage power plants, nuclear reactors, and other renewable energy sources. They can optimize power generation, minimize maintenance costs, and ensure safe operation.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, plc controllers play a crucial role in modern industrial systems. They are capable of handling complex tasks, optimizing production processes, and ensuring safe operations. As technology continues to advance, the demand for efficient and reliable plc controllers will only increase. Therefore, investing in quality plc controllers is essential for businesses looking to stay competitive in the market.
Content expansion reading:
Articles related to the knowledge points of this article:
PLC Controller Wiring Guideline
How to Use a PLC Controller for Your Business
PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) Control System Basics
Plumbers Rule! The Role of PLC Controllers in the World of Waterworks
The Role of Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) in Foreign Trade Operations